Chinese EVs can overcome headwinds in global markets
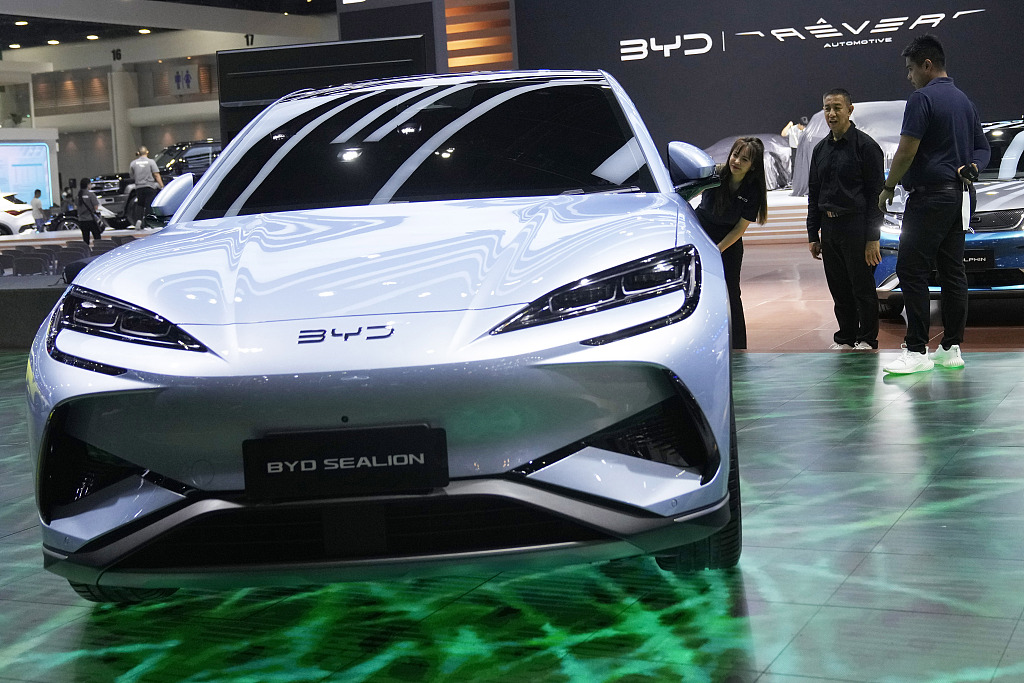


China's electric vehicle (EV) industry has become increasingly competitive in the global market thanks to the country making rapid advancements in EV technology, manufacturing capability and quality production. Official data show China's EV production and sales in 2023 reached 9.58 million and 9.49 million respectively, both highest in the world for nine straight years. China also exported 1.20 million EVs in 2023, a year-on-year increase of 77.6 percent.
The main reason why Chinese-made EVs have become popular is cost competitiveness. And cost competitiveness is partly driven by economies of scale, efficient manufacturing and government support. The large market size and the home market effect have allowed Chinese EV makers to achieve economies of scale, reduce production costs, and sell their products at competitive prices.
Also, China has made significant strides in EV technology, particularly in areas such as battery technology, electric drivetrains and other connectivity features. Chinese EV makers have also developed competitive electric power trains and battery packs, and built charging infrastructure, contributing to the overall competitiveness of Chinese-made EVs.
China's shift toward electric vehicles is largely driven by its environmental commitments — to peak its carbon dioxide emissions before 2030 and achieve carbon neutrality before 2060. The country has also built the world's largest charging infrastructure system in terms of number, largest radiation area and most comprehensive service vehicles. And the government's support in the form of investment in the charging infrastructure network has promoted the rapid development of EVs.
However, the international success of Chinese-made EVs has increased the concerns of the US and European Union countries, with some of them resorting to protectionist measures, including imposing extra tariffs on Chinese-made EVs, to safeguard their own automobile industries. In October 2023, for example, the European Commission launched an anti-subsidy investigation into the imports of battery-driven electric vehicles (BEVs) from China, apparently to determine if they benefit from excessive government subsidies which could harm BEV makers in the EU.
Besides, last month, US President Biden initiated measures to prevent Chinese-made EVs from entering the US on the pretext of safeguarding national security, claiming they could collect sensitive data of users. The probe may lead to the US imposing additional restrictions on importing vehicles that rely on Chinese software.
Such efforts to restrict the import of EVs reflect the broader political and economic concerns of the US and EU policymakers about China.
First, both the US and the EU regard large-capacity EV battery making units as strategic sectors and say the industries are related to its overall competitiveness. While the US has passed the Inflation Reduction Act to provide discriminatory subsidies for EV assembly lines, the EU has enacted battery-related regulations and raised the requirements for battery makers to export their products to the EU.
Second, major economies, including the US, are paying greater attention to strengthen their supply chains so as to reduce the vulnerability and safeguard national security. China's increasing global market share in EVs and large-capacity battery components has drawn attention to supply chain policies amid anti-globalization sentiments.
Third, many US- and EU-based fossil-fuel car makers are skeptical about EVs, because the impact of EVs on economies has heightened labor conflicts within the traditional auto sectors in the US and Europe. Consequently, influenced by these interest groups, the US and the EU might consider implementing more protectionist measures against imported EVs or battery components.
Electric vehicles have many advantages compared with fossil fuel-operated vehicles, such as environmental benefits, reduced operating costs, enhanced driving experience, and technological advancements. These advantages make China a global leader in EVs, and given the global success of Chinese-made EVs, the US and the EU cannot win the competition by resorting to protectionist trade policies.
If the Western countries impose punitive tariffs on Chinese-made EVs, they will unwittingly raise EV prices for their consumers, and protectionist measures that aim to shield domestic companies from competition may hinder innovation and lead to inefficiency, especially in an industry that relies heavily on technological advancements.
Fourth, protectionist policies will hinder the countries' efforts to reduce emissions, and weaken the global fight against climate change. Protectionist measures that limit a country's access to international markets or EV technologies may slow down the global progress in addressing climate change, prompting people to question the legitimacy of protecting "domestic industries" amid the growing need to address climate change.
And fifth, hindering competition or even cracking down on foreign companies for political reasons such as on the pretext of safeguarding national security will make people wonder whether the market in some developed countries is as free and open as they claim.
Technological advancements in the EV sector can only be achieved through cooperation and fair competition. Political strategies based solely on competition among major powers will not only restrict the development of EVs but also undermine global emissions reduction efforts. Policymakers should carefully consider these factors before taking any climate decision.
The author is an associate researcher at the Institute of American Studies, Chinese Academy of Social Sciences.
The views don't necessarily represent those of China Daily.
If you have a specific expertise, or would like to share your thought about our stories, then send us your writings at [email protected], and [email protected].