Expert on Mayan culture sees similarities in Sanxingdui relics


Discoveries at the famous Sanxingdui ruins in Southwest China show that the region's ancient Shu state civilization shared similarities with the Maya, according to the director of the Chichen Itza archaeological site, Marco Antonio Santos.
The Sanxingdui ruins, located in the city of Guanghan, about 60 kilometers from Chengdu, the provincial capital of Sichuan, belonged to the Shu Kingdom that existed at least 4,800 years ago and lasted more than 2,000 years.
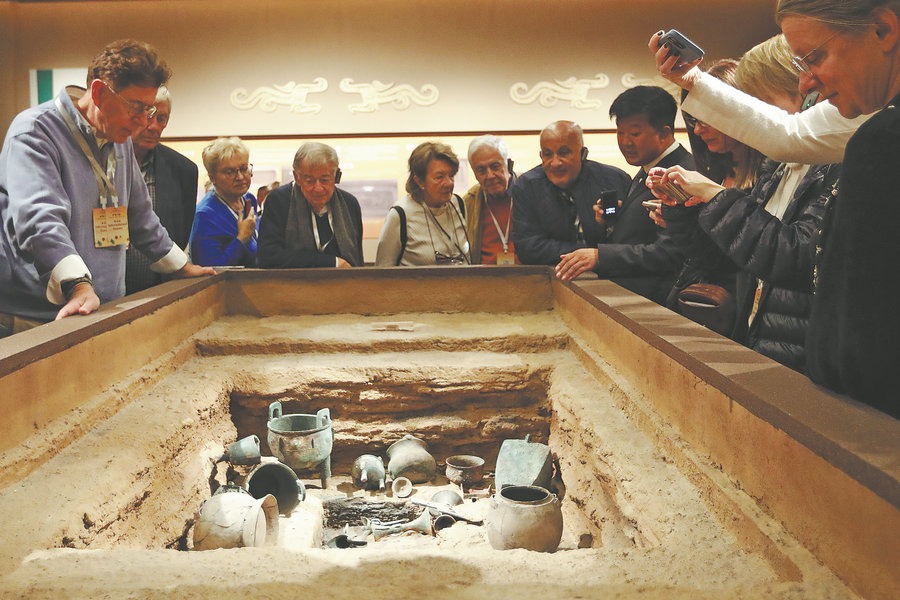
China announced on March 20 that archaeologists had uncovered gold, ivory and jade objects dating back about 3,000 years in six newly-unearthed sacrificial pits.
The Mayan civilization built its city-states around 200 AD. The pre-Hispanic city of Chichen Itza, a key Mayan ceremonial center featuring the famed Kukulcan pyramid as an important totem for the Maya people, existed from approximately 700 to 1200 AD.
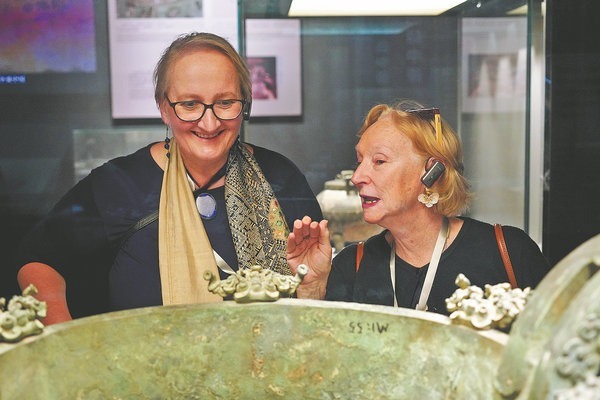
Santos says that the bronze-made remnants of trees buried in sacrificial pits at the ruins of the Shu Kingdom resembles the sacred ceiba tree, which symbolized the union of heaven, earth and the underworld in the Mayan civilization that flourished in Mesoamerica.
"They are very important similarities," said Santos, stressing that "the representations of trees in both cultures provides a symbolism that is very similar".
The findings at the Sanxingdui ruins, considered one of the greatest archaeological discoveries of the 20th century, also show a new aspect of bronze-age culture, indicating the ancient civilization already had knowledge of technologies that were thought to have been developed much later, says Santos.
While the time span between the millennial Shu Kingdom and the Mayan culture that flourished in the jungles of southeast Mexico is great, the findings highlight the closeness between the two civilizations, says Santos.
They developed in regions with comparable climates and reflected their worldview through related symbols, he notes, adding that among the over 500 artifacts recently unearthed in Sanxingdui, were pieces of gold and jade, materials the Maya also used to represent elements related to royalty and the gods.